

Stanislaus, “Spent catalyst waste management: A review: Part I-Developments in hydroprocessing catalyst waste reduction and use”, Resources, Conservation and Recycling, Vol. Dufresne, “Hydroprocessing catalysts regeneration and recycling”, Appl. Silvy, “Future trends in refining catalyst market”, Appl. Reddy.,”Nickel recovery from spent Raneynickel catalyst through dilute sulfuric acid leaching and soda ash precipitation”, Journal of Hazardous Materials, Vol. 100% efficiency was achieved at 140 ☌ for 120 minutes, nitric acid concentration of 1.5 mm, Rpm of 600 and 40 s/l 40 grams per liter.Ĭatalyst, high-pressure hydrogenation, nitric acid, nickel In this study, the parameters of temperature, concentration, time and Rpm were studied using pressurized dissolving method. The present research studied the Nickel recovery from spent catalysts of NiO/Al2O¬3 used in reduction gas reliefs of the production of sponge iron unit. Through the hydrometallurgy method, the present study investigates a possible solution to the problem of catalyst depot (due to heavy metals such as nickel) via nickel recovery, which may increase the possibility of selling or re-using the precious and expensive metal.
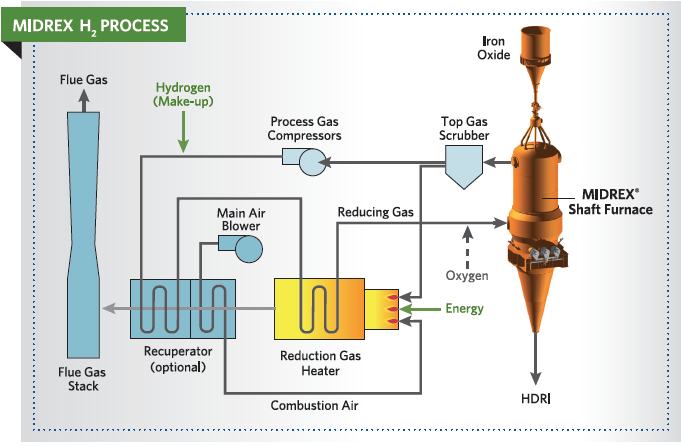
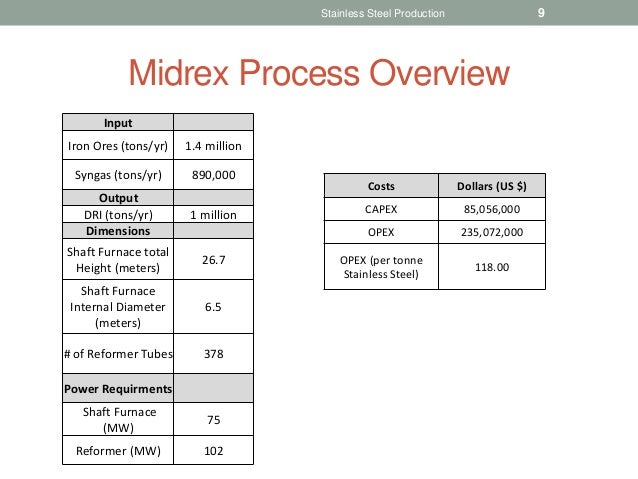
Thus, the problem of spent catalysts will become a serious environmental challenge. The steel industry in Iran hopes to employ the MIDREX technique for the 80 percent of the 50 million tons of steel. As an expensive material used in MIDREX method for steel units, this type of catalyst has major environmental problems after accumulation. In the process of direct reduction of iron pellet and production of sponge iron, NiO/Al2O3 act as a catalyst for the generation of carbon monoxide and hydrogen by vapor and natural gas.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
